上一篇介绍了顺序表及初始化的过程,本节学习有关顺序表的一些基本操作,以及如何使用 C 语言实现它们。
顺序表插入元素向已有顺序表中插入数据元素,根据插入位置的不同,可分为以下 3 种情况:- 插入到顺序表的表头;
- 在表的中间位置插入元素;
- 尾随顺序表中已有元素,作为顺序表中的最后一个元素;
虽然数据元素插入顺序表中的位置有所不同,但是都使用的是同一种方式去解决,即:通过遍历,找到数据元素要插入的位置,然后做如下两步工作:- 将要插入位置元素以及后续的元素整体向后移动一个位置;
- 将元素放到腾出来的位置上;
例如,在 {1,2,3,4,5} 的第 3 个位置上插入元素 6,实现过程如下:- 遍历至顺序表存储第 3 个数据元素的位置,如图 1 所示:
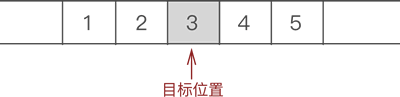
图 1 找到目标元素位置
- 将元素 3 以及后续元素 4 和 5 整体向后移动一个位置,如图 2 所示:
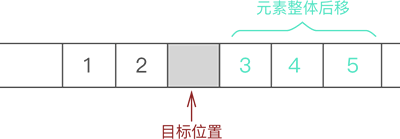
图 2 将插入位置腾出
- 将新元素 6 放入腾出的位置,如图 3 所示:
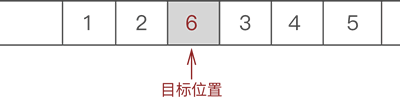
图 3 插入目标元素
因此,顺序表插入数据元素的 C 语言实现代码如下:- //插入函数,其中,elem为插入的元素,add为插入到顺序表的位置
- table addTable(table t,int elem,int add)
- {
- //判断插入本身是否存在问题(如果插入元素位置比整张表的长度+1还大(如果相等,是尾随的情况),或者插入的位置本身不存在,程序作为提示并自动退出)
- if (add>t.length+1||add<1) {
- printf("插入位置有问题\n");
- return t;
- }
- //做插入操作时,首先需要看顺序表是否有多余的存储空间提供给插入的元素,如果没有,需要申请
- if (t.length==t.size) {
- t.head=(int *)realloc(t.head, (t.size+1)*sizeof(int));
- if (!t.head) {
- printf("存储分配失败\n");
- return t;
- }
- t.size+=1;
- }
- //插入操作,需要将从插入位置开始的后续元素,逐个后移
- for (int i=t.length-1; i>=add-1; i--) {
- t.head[i+1]=t.head[i];
- }
- //后移完成后,直接将所需插入元素,添加到顺序表的相应位置
- t.head[add-1]=elem;
- //由于添加了元素,所以长度+1
- t.length++;
- return t;
- }
注意,动态数组额外申请更多物理空间使用的是 realloc 函数。并且,在实现后续元素整体后移的过程,目标位置其实是有数据的,还是 3,只是下一步新插入元素时会把旧元素直接覆盖。
顺序表删除元素从顺序表中删除指定元素,实现起来非常简单,只需找到目标元素,并将其后续所有元素整体前移 1 个位置即可。
后续元素整体前移一个位置,会直接将目标元素删除,可间接实现删除元素的目的。
例如,从 {1,2,3,4,5} 中删除元素 3 的过程如图 4 所示:
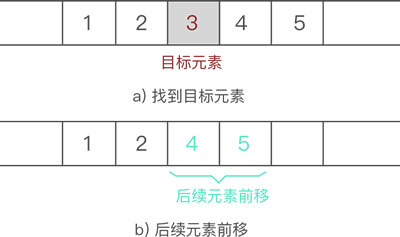
图 4 顺序表删除元素的过程示意图
因此,顺序表删除元素的 C 语言实现代码为:
- table delTable(table t,int add){
- if (add>t.length || add<1) {
- printf("被删除元素的位置有误\n");
- return t;
- }
- //删除操作
- for (int i=add; i<t.length; i++) {
- t.head[i-1]=t.head[i];
- }
- t.length--;
- return t;
- }
顺序表查找元素顺序表中查找目标元素,可以使用多种查找算法实现,比如说二分查找算法、插值查找算法等。
这里,我们选择顺序查找算法,具体实现代码为:- //查找函数,其中,elem表示要查找的数据元素的值
- int selectTable(table t,int elem){
- for (int i=0; i<t.length; i++) {
- if (t.head[i]==elem) {
- return i+1;
- }
- }
- return -1;//如果查找失败,返回-1
- }
顺序表更改元素顺序表更改元素的实现过程是:
顺序表更改元素的 C 语言实现代码为:- //更改函数,其中,elem为要更改的元素,newElem为新的数据元素
- table amendTable(table t,int elem,int newElem){
- int add=selectTable(t, elem);
- t.head[add-1]=newElem;//由于返回的是元素在顺序表中的位置,所以-1就是该元素在数组中的下标
- return t;
- }
以上是顺序表使用过程中最常用的基本操作,这里给出本节完整的实现代码:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define Size 5
- typedef struct Table{
- int * head;
- int length;
- int size;
- }table;
- table initTable(){
- table t;
- t.head=(int*)malloc(Size*sizeof(int));
- if (!t.head)
- {
- printf("初始化失败\n");
- exit(0);
- }
- t.length=0;
- t.size=Size;
- return t;
- }
- table addTable(table t,int elem,int add)
- {
- if (add>t.length+1||add<1) {
- printf("插入位置有问题\n");
- return t;
- }
- if (t.length>=t.size) {
- t.head=(int *)realloc(t.head, (t.size+1)*sizeof(int));
- if (!t.head) {
- printf("存储分配失败\n");
- }
- t.size+=1;
- }
- for (int i=t.length-1; i>=add-1; i--) {
- t.head[i+1]=t.head[i];
- }
- t.head[add-1]=elem;
- t.length++;
- return t;
- }
- table delTable(table t,int add){
- if (add>t.length || add<1) {
- printf("被删除元素的位置有误\n");
- return t;
- }
- for (int i=add; i<t.length; i++) {
- t.head[i-1]=t.head[i];
- }
- t.length--;
- return t;
- }
- int selectTable(table t,int elem){
- for (int i=0; i<t.length; i++) {
- if (t.head[i]==elem) {
- return i+1;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- table amendTable(table t,int elem,int newElem){
- int add=selectTable(t, elem);
- t.head[add-1]=newElem;
- return t;
- }
- void displayTable(table t){
- for (int i=0;i<t.length;i++) {
- printf("%d ",t.head[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- int main(){
- table t1=initTable();
- for (int i=1; i<=Size; i++) {
- t1.head[i-1]=i;
- t1.length++;
- }
- printf("原顺序表:\n");
- displayTable(t1);
- printf("删除元素1:\n");
- t1=delTable(t1, 1);
- displayTable(t1);
- printf("在第2的位置插入元素5:\n");
- t1=addTable(t1, 5, 2);
- displayTable(t1);
- printf("查找元素3的位置:\n");
- int add=selectTable(t1, 3);
- printf("%d\n",add);
- printf("将元素3改为6:\n");
- t1=amendTable(t1, 3, 6);
- displayTable(t1);
- return 0;
- }
程序运行结果为:原顺序表:
1 2 3 4 5
删除元素1:
2 3 4 5
在第2的位置插入元素5:
2 5 3 4 5
查找元素3的位置:
3
将元素3改为6:
2 5 6 4 5






